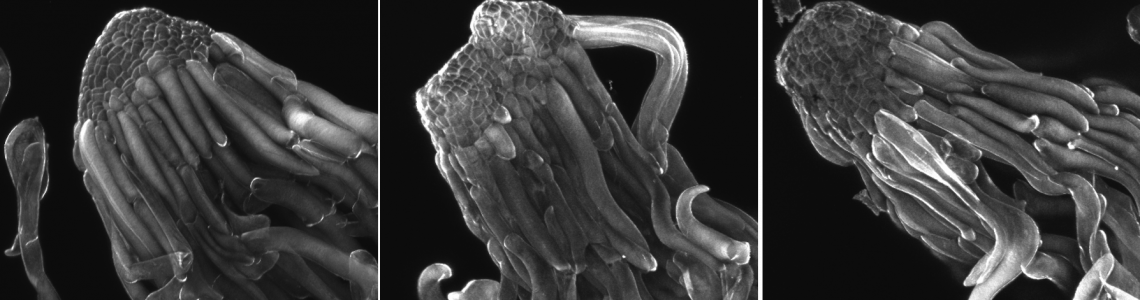
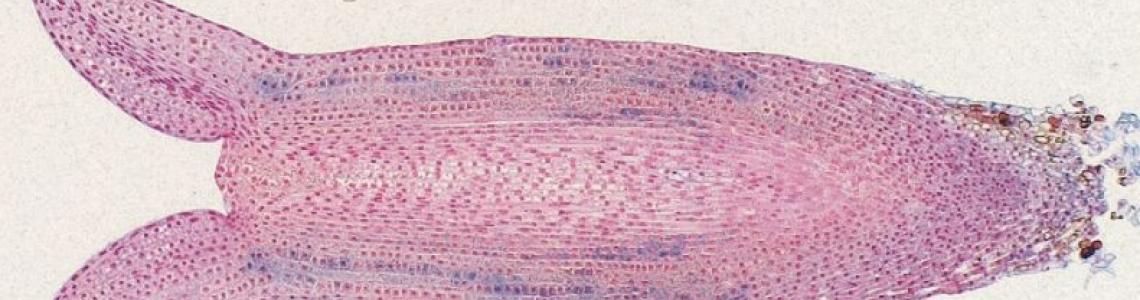
The effect of drought stress on Norway spruce somatic embryo development
Somatic embryogenesis is a developmental process where a plant somatic cell dedifferentiate to a totipotent embryonic stem cell that has the ability to give rise to an embryo under appropriate conditions. Desiccation is the final phase of normal embryonic development in most angiosperms and appears to be important in the transition from embryogeny to the ability to germinate and form normal seedlings.