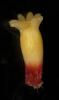
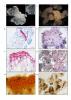
Multi-scale characterizations of various desiccation treatments to produce somatic embryos closer to zygotic embryos of hybrid larch.
Somatic embryogenesis is a useful method for propagating selected plant material. However, before using this technique for forest tree deployment, it is important to ensure high-quality somatic embryos (SEs). This quality depends on how closely SEs resemble zygotic embryos (ZEs). At the end of their maturation, SEs usually resemble ZEs from fresh seeds due to their high water content and biochemical composition.