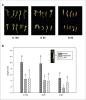
The humidity level matters during the desiccation of Norway spruce somatic embryos
In Norway spruce, as in many other conifers, the germination capacity of somatic embryos is strongly influenced by the desiccation phase inserted after maturation. The intensity of drying during desiccation eminently affected the formation of emblings (i.e., seedlings developed from somatic embryos). Compared to non-desiccated embryos, the germination capacity of embryos desiccated at 100% relative humidity was about three times higher, but the reduction of relative humidity to 95% and 90% had a negative effect on the subsequent embryo development.