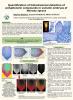
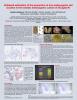
Quantification of histochemical detection of polyphenolic compounds in somatic embryos of Norway spruce
Under standard cultivation conditions, Norway spruce somatic embryos (SEs) accumulate polyphenolic compounds mostly in the root cap. In response to UV-B, the accumulation of polyphenolics increases in protodermal cells and subprotodermal cortical cells and idioblasts in hypocotyl and cotyledons where they can attenuate UV-B stress. To quantify polyphenolic compounds accumulated in somatic embryos on the histological level resin sections were prepared, stained with Toluidine Blue.