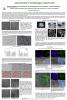
Assessment of autophagy in plant cells
Autophagy is an evolutionary conserved catabolic process deemed to maintain or restore cellular and organismal homeostasis. In plants, basal autophagy is essential for growth and development, it is required for nutrient remobilization during senescence and nutrient deficiency, for removal of organelles and macromolecules formed during plant development or damaged by environmental stresses.