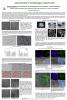
Wholemount immunolabeling and stereological quantification of autophagosomes in Arabidopsis thaliana root epidermal cells
The workflow enables the quantification of autophagosomes in Arabidopsis thaliana root epidermal cells in 3D. It combines immunolabeling of an autophagosome marker ATG8 with commercially available anti-ATG antibody and the subsequent stereological quantification of the immunolabeled particles. The immunolabeled samples are imaged with a confocal microscope and Z-stacks are acquired.