About
Our research group mainly studies the metabolism and physiological functions of growth regulators, polyamines, and phenolic compounds in plants. We investigate the role of these biologically active compounds in plant development and in the response of plants to abiotic stresses.
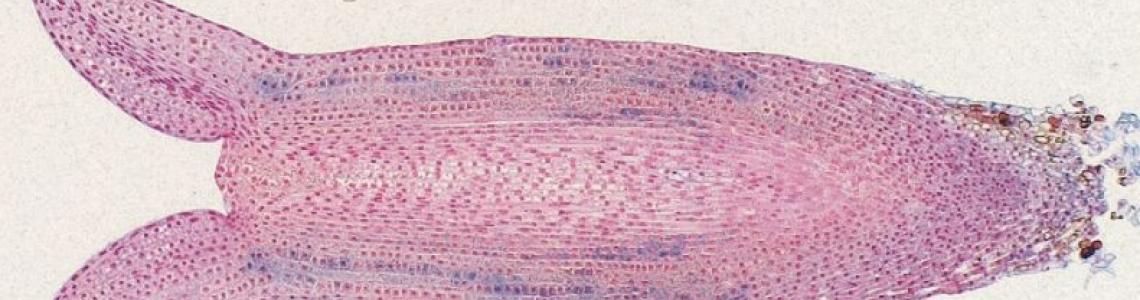
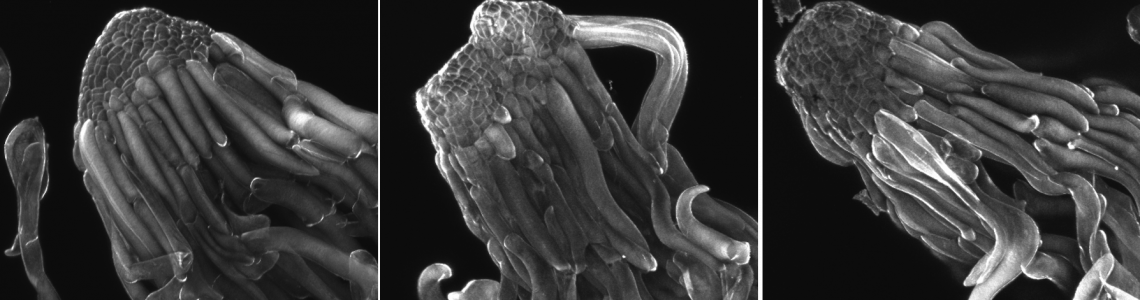
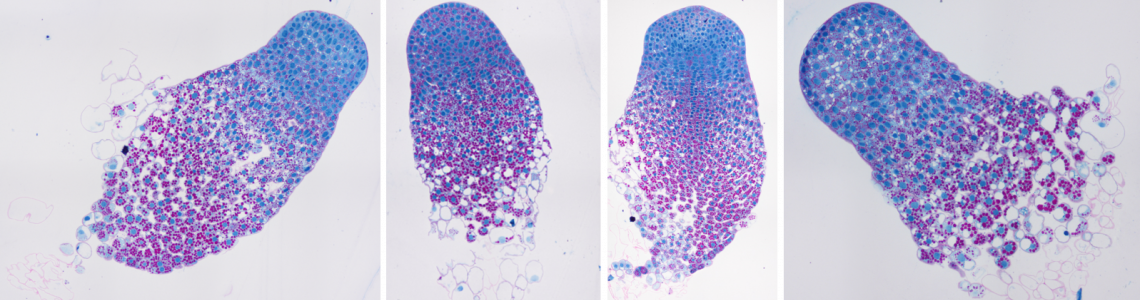
In our experiments, we use diverse plant systems from whole plants to cell cultures. Our research is primarily focused on the somatic embryogenesis of conifers. Within this topic, we study the regulation of somatic embryo development, the role of phytohormones in somatic embryogenesis, and the effects of abiotic stresses on somatic embryos. We also deal with the in vitro propagation of medicinal cannabis. In particular, we investigate the effect of phytohormones (auxins and cytokinins) added to the culture medium on the process of organogenesis from segments of cannabis plants grown from seeds in vitro.
We use a wide array of approaches:
-
Microscopy – light, confocal, and electron microscopy, enhanced by advanced computer image analysis
-
Biochemical methods – studies of activities of enzymes involved in the metabolism of biologically active compounds (e.g. radiometry)
-
Molecular biology methods – specific gene expressions, and transformation of tissue cultures
-
Analytical methods – qualitative and quantitative determination of biologically active compounds by gas- and liquid chromatography in tandem with mass spectroscopic detection (cooperation with the IEB Laboratory of Growth Regulators and Laboratory of Hormonal Regulations in Plants).